Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamamoto, Yusuke*; Watanabe, Takahiro; Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Koji
JAEA-Testing 2023-003, 67 Pages, 2024/02
A long-term geosphere stability for geological disposal is evaluated by the past geological environmental changes and modern conditions. Stable hydrogen and oxygen isotope ratios ( D,
D, 
 O) of geological samples are useful information to estimate the past environmental changes and modern conditions. Recently, the thermal conversion elemental analyzer and isotope ratio mass spectrometer (TC-EA/IRMS) were installed in the Tono Geoscience Center for
O) of geological samples are useful information to estimate the past environmental changes and modern conditions. Recently, the thermal conversion elemental analyzer and isotope ratio mass spectrometer (TC-EA/IRMS) were installed in the Tono Geoscience Center for  D and
D and 
 O measurements of geological samples. In this study, we reported analytical methods of
O measurements of geological samples. In this study, we reported analytical methods of  D and
D and 
 O using international standard reference materials. In addition, evaluation tests of uncertainty by repeated analyses of the standards were performed using the TC-EA/IRMS. Furthermore, the
O using international standard reference materials. In addition, evaluation tests of uncertainty by repeated analyses of the standards were performed using the TC-EA/IRMS. Furthermore, the  D and
D and 
 O analyses by the TC- EA/IRMS were also applied to fault rock samples.
O analyses by the TC- EA/IRMS were also applied to fault rock samples.
 high energy resolution XAFS
high energy resolution XAFSYamamoto, Naoki*; Matsumura, Daiju; Hagihara, Yuto*; Tanaka, Kei*; Hasegawa, Yuta*; Ishii, Kenji*; Tanaka, Hirohisa*
Journal of Power Sources, 557, p.232508_1 - 232508_10, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:29.01(Chemistry, Physical) , ThO
, ThO , UO
, UO , PuO
, PuO , and (U, Pu)O
, and (U, Pu)O
Kato, Masato; Watanabe, Masashi; Hirooka, Shun; Vauchy, R.
Frontiers in Nuclear Engineering (Internet), 1, p.1081473_1 - 1081473_10, 2023/01
 (001) surface with supersonic seeded oxygen molecular beam
(001) surface with supersonic seeded oxygen molecular beamKatsube, Daiki*; Ono, Shinya*; Inami, Eiichi*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Abe, Masayuki*
Vacuum and Surface Science, 65(11), p.526 - 530, 2022/11
The oxidation of oxygen vacancies at the surface of anatase TiO (001) was investigated by synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy and supersonic O
(001) was investigated by synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy and supersonic O beam (SSMB). The oxygen vacancies at the top surface and subsurface could be eliminated by the supply of hyperthermal oxygen molecules. Oxygen vacancies are present on the surface of anatase TiO
beam (SSMB). The oxygen vacancies at the top surface and subsurface could be eliminated by the supply of hyperthermal oxygen molecules. Oxygen vacancies are present on the surface of anatase TiO (001) when it is untreated before transfer to a vacuum chamber. These vacancies, which are stable in the ambient condition, could also be effectively eliminated by using oxygen SSMB. This result is promising as a surface processing for various functional oxides.
(001) when it is untreated before transfer to a vacuum chamber. These vacancies, which are stable in the ambient condition, could also be effectively eliminated by using oxygen SSMB. This result is promising as a surface processing for various functional oxides.
Liu, B.*; Feng, R.*; Busch, M.*; Wang, S.*; Wu, H.*; Liu, P.*; Gu, J.*; Bahadoran, A.*; Matsumura, Daiju; Tsuji, Takuya; et al.
ACS Nano, 16(9), p.14121 - 14133, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:51 Percentile:98.33(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary) based on experimental data and density functional theory calculation result
based on experimental data and density functional theory calculation resultWatanabe, Masashi; Nakamura, Hiroki; Suzuki, Kiichi; Machida, Masahiko; Kato, Masato
Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 105(3), p.2248 - 2257, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.98(Materials Science, Ceramics)Properties of CeO were evaluated by DFT simulation to determine band gap, Frenkel defect formation energy and defect migration energy. Band gap and Frenkel defect formation energy were used to analyze defect equilibria. Oxygen partial pressure dependence of defect equilibria was evaluated based on oxygen potential experimental data and DFT calculation, and a Brouwer diagram was derived. The defect formation energies, including Frenkel defect, electron-hole pair and so on, were determined and used to evaluate the properties, including oxygen diffusion coefficients, electrical conduction, heat capacity and thermal conductivity. Mechanisms of various properties were discussed for a deeper understanding based on defect chemistry, and the relationship among properties were systematically described.
were evaluated by DFT simulation to determine band gap, Frenkel defect formation energy and defect migration energy. Band gap and Frenkel defect formation energy were used to analyze defect equilibria. Oxygen partial pressure dependence of defect equilibria was evaluated based on oxygen potential experimental data and DFT calculation, and a Brouwer diagram was derived. The defect formation energies, including Frenkel defect, electron-hole pair and so on, were determined and used to evaluate the properties, including oxygen diffusion coefficients, electrical conduction, heat capacity and thermal conductivity. Mechanisms of various properties were discussed for a deeper understanding based on defect chemistry, and the relationship among properties were systematically described.
Kimata, Tetsuya*; Kakitani, Kenta*; Yamamoto, Shunya*; Shimoyama, Iwao; Matsumura, Daiju; Iwase, Akihiro*; Mao, W.*; Kobayashi, Tomohiro*; Yamaki, Tetsuya*; Terai, Takayuki*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 6(3), p.035801_1 - 035801_7, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:71.37(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Otani, Kyohei; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Kato, Chiaki
Zairyo To Kankyo, 71(2), p.40 - 45, 2022/02
The purpose of this study is to investigate the effect of oxygen concentration in the air on the corrosion rate of carbon steel in an air/solution alternating environment in the low oxygen concentration range and to clarify the corrosion rate and corrosion mechanism of carbon steel depending on the oxygen concentration in air by the mass change of specimens before and after the corrosion test and observing the iron rust layer formed on the surface of carbon steel. The corrosion rate increases with increasing oxygen concentration in the air, and the gradient of the corrosion rate decreases gradually. The maximum erosion depth increased with increasing oxygen concentration except for the case of 1% oxygen concentration, however, the maximum erosion depth for 1% oxygen concentration was larger than that for 5% air oxygen concentration.
Nagai, Takayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Yamagishi, Hirona*; Ota, Toshiaki*; Kojima, Kazuo*; Inose, Takehiko*; Sato, Seiichi*; Hatakeyama, Kiyoshi*
JAEA-Research 2021-010, 62 Pages, 2022/01
The local structure of glass-forming elements and waste elements in borosilicate glasses varies with its chemical composition. In this study, borosilicate glass frit and simulated waste glass samples were prepared and the local structure and chemical state regarding boron(B), oxygen(O), silicon(Si) and waste elements of iron(Fe), cesium(Cs) were estimated by using XAFS measurement in soft X-ray region. Following results were obtained by XAFS measurements of prepared glass frit and simulated waste glass samples: (1) The effect of Na O concentration on B-O coordination structure is greater than that of the waste elements concentration. (2) The height of pre-edge by O K-edge spectrum depends on the concentration of first transition elements such as Fe in glass samples. Following results were obtained by XAFS measurements of simulated waste glass samples after immersion test to investigate the long chemical stability. (1) A new compound was formed on the sample surface after the immersion test, and changes in the surface state were confirmed by Raman spectroscopy. (2) Cs on the sample surface after immersion test dissolves into the leaching solution. The Si K-edge XANES spectra of borosilicate glass frits and simulated waste glass samples included lanthanides oxide were measured, and following was confirmed. (1) As the Na
O concentration on B-O coordination structure is greater than that of the waste elements concentration. (2) The height of pre-edge by O K-edge spectrum depends on the concentration of first transition elements such as Fe in glass samples. Following results were obtained by XAFS measurements of simulated waste glass samples after immersion test to investigate the long chemical stability. (1) A new compound was formed on the sample surface after the immersion test, and changes in the surface state were confirmed by Raman spectroscopy. (2) Cs on the sample surface after immersion test dissolves into the leaching solution. The Si K-edge XANES spectra of borosilicate glass frits and simulated waste glass samples included lanthanides oxide were measured, and following was confirmed. (1) As the Na O concentration increases in borosilicate glass frit, the K-edge peak of Si shifts to the low energy side. (2) The peak height of the K-edge of Si differs depending on the kind of lanthanide.
O concentration increases in borosilicate glass frit, the K-edge peak of Si shifts to the low energy side. (2) The peak height of the K-edge of Si differs depending on the kind of lanthanide.
 with Pu = 0.45 and 0.68 and related defect formation energy
with Pu = 0.45 and 0.68 and related defect formation energyHirooka, Shun; Matsumoto, Taku; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Hino, Tetsushi*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 558, p.153375_1 - 153375_8, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:31.78(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Sasa, Toshinobu
Kasokuki, 18(4), p.233 - 240, 2022/01
Lead bismuth eutectic alloy (LBE) is a promising option as a spallation target for accelerator-driven transmutation systems (ADS) to reduce the radiological toxicity from long-lived radioactive waste. LBE is a heavy metal and has suitable characteristics both as a spallation target and as a coolant for transmutation systems. However, LBE is also known as a highly corrosive with structural materials. In this paper, technological developments to overcome the issue, the latest research activities such as hightemperature operation and oxygen concentration control to ensure corrosion resistance, are introduced together with the outline of the target for ADS.
 (001) surface using supersonic seeded oxygen molecular beam
(001) surface using supersonic seeded oxygen molecular beamKatsube, Daiki*; Ono, Shinya*; Takayanagi, Shuhei*; Ojima, Shoki*; Maeda, Motoyasu*; Origuchi, Naoki*; Ogawa, Arata*; Ikeda, Natsuki*; Aoyagi, Yoshihide*; Kabutoya, Yuito*; et al.
Langmuir, 37(42), p.12313 - 12317, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.77(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We investigated the oxidation of oxygen vacancies at the surface of anatase TiO (001) using supersonic seeded molecular beam (SSMB) of oxygen. The oxygen vacancies at the top-surface and sub-surface could be eliminated by the supply of oxygen using an SSMB. These results indicate that the interstitial vacancies can be mostly assigned to oxygen vacancies, which can be effectively eliminated by using an oxygen SSMB. Oxygen vacancies are present on the surface of anatase TiO
(001) using supersonic seeded molecular beam (SSMB) of oxygen. The oxygen vacancies at the top-surface and sub-surface could be eliminated by the supply of oxygen using an SSMB. These results indicate that the interstitial vacancies can be mostly assigned to oxygen vacancies, which can be effectively eliminated by using an oxygen SSMB. Oxygen vacancies are present on the surface of anatase TiO (001) when it is untreated before transfer to a vacuum chamber. These vacancies, which are stable in the as-grown condition, could also be effectively eliminated using the oxygen SSMB.
(001) when it is untreated before transfer to a vacuum chamber. These vacancies, which are stable in the as-grown condition, could also be effectively eliminated using the oxygen SSMB.
Saito, Shigeru; Wan, T.*; Okubo, Nariaki; Obayashi, Hironari; Watanabe, Nao; Ohdaira, Naoya*; Kinoshita, Hidetaka; Yamaki, Kenichi*; Kita, Satoshi*; Yoshimoto, Hidemitsu*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011041_1 - 011041_6, 2021/03
An Accelerator Driven System (ADS) for waste transmutation investigated in JAEA employs lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE) as a neutron production target material and coolant. The neutrons are to be produced via the spallation with 1.5 GeV proton beam injection. As materials irradiation data are important for ADS development, JAEA plans to construct an irradiation facility with LBE neutron production target in J-PARC. There are many technical issues on LBE for practical use. In JAEA, various R&Ds are being carried out. Concerning corrosion study, conditioning operation and functional tests of OLLOCHI started. Oxygen concentration control technology has also developing. In the large scale LBE loop experiment, the operation for steady state and transient experiments was performed by using IMMORTAL. In the area of instrument, development of ultrasonic flow meter and freeze seal valve are progressing as a key technology for the LBE loop system. Investigation of behavior of impurities in LBE, which is important for design of the irradiation facility, started. In this paper, the status of the LBE studies and experimental plan will be presented.
Sasa, Toshinobu; Saito, Shigeru; Obayashi, Hironari; Ariyoshi, Gen
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011051_1 - 011051_6, 2021/03
To realize Accelerator-driven system (ADS) for minor actinide transmutation, JAEA proposes to construct the Proton Irradiation Facility in J-PARC. The facility is planned to solve technical issues for safe application of Lead-bismuth Eutectic Alloy (LBE). The 250 kW LBE spallation target will be located in the facility to prepare material irradiation database by both proton and neutron irradiation in the temperature range for typical LBE-cooled ADS. Various studies for important technologies required to build the facilities are investigated such as oxygen concentration control, instruments development, remote handling techniques for target maintenance, and spallation target design. The large scale LBE loops for mock up the 250 kW LBE spallation target and material corrosion studies are also manufactured and applied to various experiments. The latest status of 250 kW LBE spallation target design works will be summarized.
Ogawa, Shuichi*; Yamaguchi, Hisato*; Holby, E. F.*; Yamada, Takatoshi*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Takakuwa, Yuji*
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), 11(21), p.9159 - 9164, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:18.31(Chemistry, Physical)Atomically thin layers of graphene have been proposed to protect surfaces through the direct blocking of corrosion reactants such as oxygen with low added weight. The long term efficacy of such an approach, however, is unclear due to the long-term desired protection of decades and the presence of defects in as-synthesized materials. Here, we demonstrate catalytic permeation of oxygen molecules through previously-described impermeable graphene by imparting sub-eV kinetic energy to molecules. These molecules represent a small fraction of a thermal distribution thus this exposure serves as an accelerated stress test for understanding decades-long exposures. The permeation rate of the energized molecules increased 2 orders of magnitude compared to their non-energized counterpart. Graphene maintained its relative impermeability to non-energized oxygen molecules even after the permeation of energized molecules indicating that the process is non-destructive and a fundamental property of the exposed material.
Nagai, Takayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Yamagishi, Hirona*; Ota, Toshiaki*; Kojima, Kazuo*; Inose, Takehiko*; Sato, Seiichi*; Hatakeyama, Kiyoshi*
JAEA-Research 2020-009, 48 Pages, 2020/09
The local structure of glass-forming elements and waste elements in waste glass varies with its chemical composition. In this study, borosilicate glass frit and simulated waste glass samples were prepared and the local structure and chemical state regarding boron (B), oxygen (O), and waste elements of cerium (Ce), cesium (Cs) were estimated by using XAFS measurement in soft X-ray region. Following results were obtained by XAFS measurements of prepared glass frit and simulated waste glass samples: (1) The existence ratio of four coordinate sp structure (BO
structure (BO ) tends to increase with increasing Na
) tends to increase with increasing Na O content in glass samples. (2) The height of a pre-edge which appears by K-edge XANES spectrum of O is so high that the Fe content in glass samples. Following results were obtained by XAFS measurements of simulated waste glass samples after immersion test to investigate long chemical stability. (1) The existence ratio of four coordinate sp
O content in glass samples. (2) The height of a pre-edge which appears by K-edge XANES spectrum of O is so high that the Fe content in glass samples. Following results were obtained by XAFS measurements of simulated waste glass samples after immersion test to investigate long chemical stability. (1) The existence ratio of four coordinate sp structure (BO
structure (BO ) increases by immersion test. (2) Ce which exists in the surface layer is oxidized by immersion test, and much of Cs in surface layer is lost after leach testing. Even if the glass frit form (fiber cartridge or beads) and manufacturing method were changed and a glass sample of the similar chemical composition was prepared, these observed Raman spectra of samples were different.
) increases by immersion test. (2) Ce which exists in the surface layer is oxidized by immersion test, and much of Cs in surface layer is lost after leach testing. Even if the glass frit form (fiber cartridge or beads) and manufacturing method were changed and a glass sample of the similar chemical composition was prepared, these observed Raman spectra of samples were different.
Ueno, Fumiyoshi
Zairyo To Kankyo, 68(1), p.2 - 8, 2019/01
It is important to control the cooling water of light water reactors (boiling water reactor and pressurized water reactor) to suitable quality in order to reduce corrosion of structural materials and generation of radioactive corrosion products. For that purpose, monitoring of water quality using electrochemical measurement method is necessary. In this article, the application of ECP measurement to BWR is mainly focused, I describe the water quality of light water reactors and the necessity of electrochemical measurement.
Okubo, Nariaki; Okuno, Yasuki; Kitamura, Akane; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 435, p.198 - 202, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:20.94(Instruments & Instrumentation)Accelerator driven system (ADS) adopts the lead-bismuth eutectic (LBE) as both coolant and spallation target. The oxygen concentration control is one of the most important technical developments. Estimation of durability under gamma-ray irradiation for the oxygen sensor is necessary for the integrity evaluation of ADS components. The Zirconia added by Yttria (YSZ) is the main element in oxygen sensor. Effect of gamma-ray irradiation on the mechanical property and structural change for three types of YSZ with 3, 6, 8 mol% Yttria was evaluated by using 4 points bend test, XRD, SEM and Raman spectroscope. The gamma-ray irradiations were conducted at 1 and 2 kGy/h, which corresponded to the LBE activity after 1 year ADS operation. In the cases of 8Y and 6Y, degradation of strength was not measured and the fracture surface did not change the morphology. In the case of 3Y, however, the strength did not change but phase transformation from tetragonal to monoclinic crystal structure was observed in XRD results, depending on the irradiation dose. This implies that the gamma-ray irradiation causes the phase transformation in 3Y-YSZ.
Yasuda, Satoshi; Uchibori, Yosuke*; Wakeshima, Makoto*; Hinatsu, Yukio*; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Yano, Masahiro; Asaoka, Hidehito
RSC Advances (Internet), 8(66), p.37600 - 37605, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:42.69(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We present a quantitative study on the effect of a newly obtained thermal history on the formation of Fe-N-C catalytic sites. A short and repeated heating process is employed as the new thermal history, where short heating (1 min) followed by quenching is applied to a sample with arbitrary repetition. Through electrochemical quantitative analysis, it is found that the new process effectively increases the Fe-N-C mass-based site density (MSD) to almost twice that achieved using a conventional continuous heating process, while the turn-over frequency (TOF) is independent of the process. Elemental analysis shows that the new process effectively suppresses the thermal desorption of Fe and N atoms during the initial formation stage and consequently contributes to an increase in the Fe-N-C site density. The resultant catalytic activity (gravimetric kinetic current density (0.8 V vs. RHE)) is 1.8 times higher than that achieved with the continuous heating process.
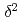 H and
H and 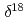 O of water in pores extracted by compression method; Effects of closed pores and comparison to direct vapor equilibration and laser spectrometry method
O of water in pores extracted by compression method; Effects of closed pores and comparison to direct vapor equilibration and laser spectrometry methodNakata, Kotaro*; Hasegawa, Takuma*; Oyama, Takahiro*; Miyakawa, Kazuya
Journal of Hydrology, 561, p.547 - 556, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:26.43(Engineering, Civil)no abstracts in English